Contents:
Image Segmentation
SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
Wei Liu, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Christian Szegedy, Scott Reed, Cheng-Yang Fu, Alexander C. Berg : Dec 2016
Source
Code
- Accurate approaches for image segmentation and object detection are available, like Faster R-CNN, but they are too slow for real time applications.
- Eliminates bounding box proposals and the subsequent pixel or feature resampling stage.
- Improvements include using a small convolutional filter to predict object categories and offsets in bounding box locations, using separate predictors (filters) for different aspect ratio detections, and applying these filters to multiple feature maps from the later stages of a network in order to perform detection at multiple scales.
- Faster than YOLO and as accurate as Faster R-CNN.
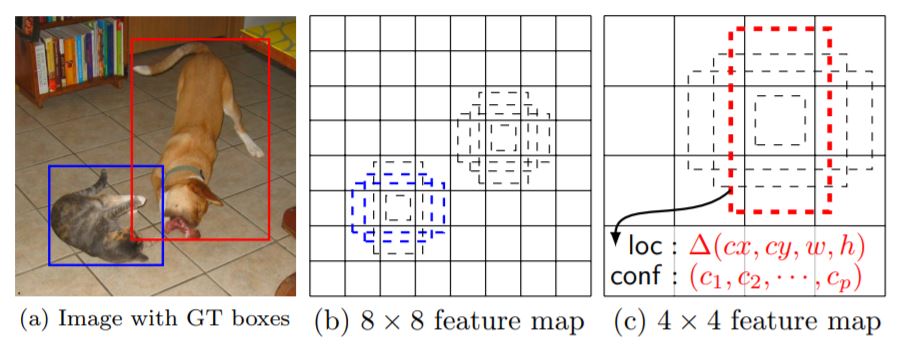 Fig. : SSD framework. (a) SSD only needs an input image and ground truth boxes for
each object during training. In a convolutional fashion, we evaluate a small set (e.g. 4)
of default boxes of different aspect ratios at each location in several feature maps with
different scales (e.g. 8 × 8 and 4 × 4 in (b) and (c)). For each default box, we predict
both the shape offsets and the confidences for all object categories \(((c_1, c_2, \cdots , c_p))\).At training time, we first match these default boxes to the ground truth boxes. For
example, we have matched two default boxes with the cat and one with the dog, which
are treated as positives and the rest as negatives. The model loss is a weighted sum
between localization loss (e.g. Smooth L1) and confidence loss (e.g. Softmax).
Fig. : SSD framework. (a) SSD only needs an input image and ground truth boxes for
each object during training. In a convolutional fashion, we evaluate a small set (e.g. 4)
of default boxes of different aspect ratios at each location in several feature maps with
different scales (e.g. 8 × 8 and 4 × 4 in (b) and (c)). For each default box, we predict
both the shape offsets and the confidences for all object categories \(((c_1, c_2, \cdots , c_p))\).At training time, we first match these default boxes to the ground truth boxes. For
example, we have matched two default boxes with the cat and one with the dog, which
are treated as positives and the rest as negatives. The model loss is a weighted sum
between localization loss (e.g. Smooth L1) and confidence loss (e.g. Softmax). - Model
- Early layers based on a standard base network.
- Multi scale feature maps for detection.
- Convolutional predictors for detection.
- Default boxes and aspect ratios, similar to anchor boxes used in Faster R-CNN.
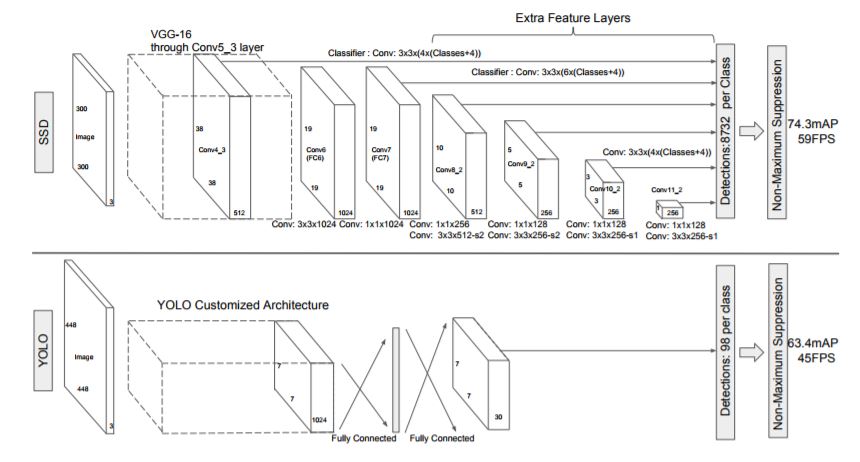
Fig. 2: A comparison between two single shot detection models: SSD and YOLO. SSD model adds several feature layers to the end of a base network, which predict the offsets to default boxes of different scales and aspect ratios and their associated confidences. SSD with a 300 × 300 input size significantly outperforms its 448 × 448 YOLO counterpart in accuracy on VOC2007 test while also improving the speed.
- Training Objective
- Let \(x_{ij}^p=\{1,0\}\) be an indicator for matching \(i\)-th default box to the \(j\)-th ground truth box of category \(p\). In the matching strategy used here, we can have \(\sum_ix{ij}^p \ge 1\). Overall loss function:
$$L(x, c, l, g) = \frac 1 N (L_{conf}(x,c) + \alpha L_{loc}(x, l, g))$$\(N = $ number of matched default boxes, $L_{loc} = $ localization loss, a smooth L1 loss between predicted box(\)l\() and ground truth(\)g$), and $L_{conf} = $ confidence loss, softmax loss over multiple classes confidences.
- Let \(x_{ij}^p=\{1,0\}\) be an indicator for matching \(i\)-th default box to the \(j\)-th ground truth box of category \(p\). In the matching strategy used here, we can have \(\sum_ix{ij}^p \ge 1\). Overall loss function:
- Data augmentation is crucial.
- More default box shapes is better.
- Multiple output layers at different resolutions is better.
OverFeat: Integrated Recognition, Localization and Detection using Convolutional Networks
Feb 2014
Source
- An integrated approach to simultaneously classify, locate and detect objects.
Comments
comments powered by Disqus